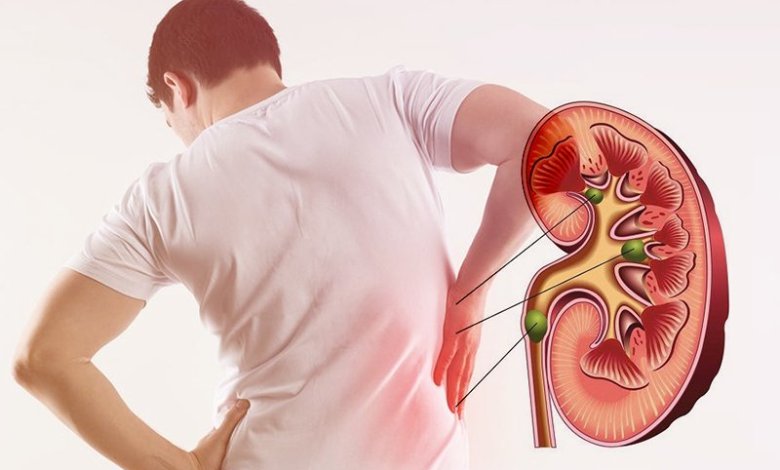
Your kidneys play an essential role in keeping your body healthy. They help filter waste, balance fluids, control blood pressure, and produce hormones. But when one or both kidneys become swollen, it’s a serious warning sign that something is wrong.
Swollen kidneys — also known as hydronephrosis — can happen when something blocks the flow of urine or causes inflammation inside the kidney. If left untreated, it can lead to infections, kidney damage, or even kidney failure.
Here are the common signs of swollen kidneys and causes you should never ignore:
Signs of Swollen Kidneys
Swollen kidneys may not always cause pain at first, but as the condition worsens, you may start noticing some of the following symptoms:
1. Pain in the Side or Lower Back
A sharp or dull pain on one or both sides of your lower back (where your kidneys are located) may indicate swelling or blockage in the kidneys.
2. Frequent Urination or Urgency
Feeling the need to urinate more often than usual — especially at night — or having trouble holding your urine can be a sign that your kidneys aren’t draining properly.
3. Pain or Burning While Urinating
If you feel pain or burning when you urinate, it could be a sign of infection or inflammation affecting the urinary tract and kidneys.
4. Blood in the Urine
Seeing pink, red, or brown urine — or noticing blood when you wipe — can be a symptom of kidney stones, infection, or other issues that may cause kidney swelling.
5. Swelling in the Legs, Face, or Abdomen
When the kidneys are swollen or not working properly, fluid may build up in other parts of the body, causing swelling especially in the ankles, feet, and around the eyes.
6. Fever or Chills (With Urinary Symptoms)
If you have a fever, chills, and pain during urination or in your lower back, it could mean a kidney infection, not just a simple UTI.
There are several medical conditions that can lead to kidney swelling, including:
1. Kidney Stones
When stones block the flow of urine, pressure builds up, leading to swelling and pain.
2. Urinary Tract Infections (Especially if Left Untreated)
Bacteria can move from the bladder up to the kidneys, causing infection and inflammation.
3. Enlarged Prostate (in Men)
An enlarged prostate can block urine flow and lead to kidney problems over time.
4. Tumors or Cysts
Growths in the urinary tract can block urine flow and cause hydronephrosis (kidney swelling).
5. Congenital Conditions
Some people are born with narrow or twisted ureters, which can block urine flow and lead to chronic swelling. View, More,
Explore More News By Using The Button.